Marketing KPIs and Attribution Models
: A Guide for Smarter Decisions
In today’s data-driven marketing world, measuring the effectiveness of campaigns isn’t just a nice-to-have it’s essential. Two pillars of performance measurement stand out: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and attribution models. Together, they help marketers understand what works, optimize budgets, and maximize ROI. But not all KPIs or attribution models are created equal. That’s where platforms like cXpify come in, providing AI-driven guidance to simplify decision-making.
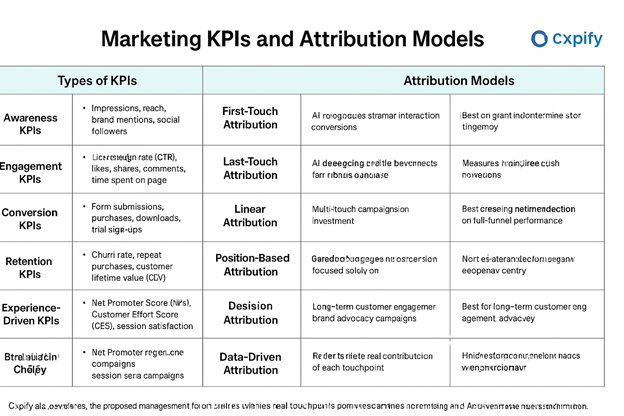
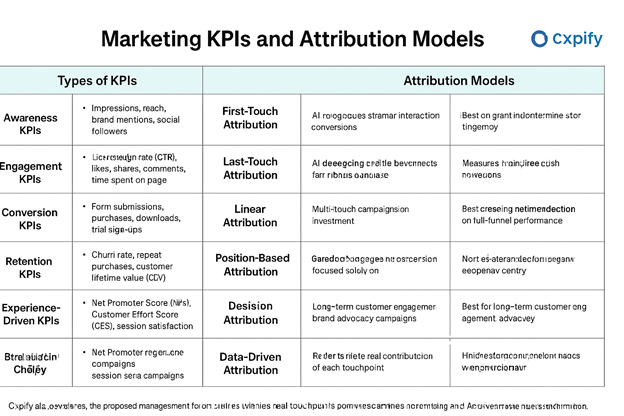
Part 1: Types of Marketing KPIs
A KPI is a measurable value that shows how effectively a company is achieving its business objectives. In marketing, KPIs can be broadly categorized into awareness, engagement, conversion, retention, and increasingly, experience-driven metrics.
1. Awareness KPIs
These measure how many people know about your brand or product.
Examples: Impressions, reach, brand mentions, social followers.
Advantages:
- Shows visibility of campaigns.
- Helps track growth in audience size.
Disadvantages: - Doesn’t measure quality of engagement or conversions.
- Can be inflated with low-value impressions.
When to use: Launching a new product or campaign.
When not to use: Evaluating direct revenue impact.
cXpify advantage: AI recommendations can highlight which channels are underperforming for awareness and suggest new engagement KPIs such as share of voice or influencer reach metrics to optimize brand visibility.
2. Engagement KPIs
Track how users interact with your content.
Examples: Click-through rate (CTR), likes, shares, comments, time spent on page.
Advantages:
- Shows audience interest and relevance of content.
- Provides qualitative insights into messaging effectiveness.
Disadvantages: - High engagement does not always translate into conversions.
When to use: Measuring content or social media effectiveness.
When not to use: Solely for evaluating sales performance.
cXpify advantage: Automatically surfaces interaction quality KPIs, such as scroll depth or micro-conversions, which traditional dashboards often overlook.
3. Conversion KPIs
Measure actions that directly impact business goals.
Examples: Form submissions, purchases, downloads, trial sign-ups.
Advantages:
- Directly linked to revenue and business outcomes.
- Easy to track ROI.
Disadvantages: - Doesn’t capture long-term brand value or customer loyalty.
When to use: Campaigns designed to drive leads or sales.
When not to use: Brand-building initiatives with no immediate conversions.
Cxpify advantage: Suggests relevant conversion KPIs based on campaign type and customer journey stage, e.g., multi-step funnel conversion or assisted conversions, so marketers don’t miss hidden revenue drivers.
4. Retention KPIs
Assess customer loyalty and repeat engagement.
Examples: Churn rate, repeat purchases, customer lifetime value (CLV).
Advantages:
- Identifies profitable customer segments.
- Supports long-term growth strategies.
Disadvantages: - Requires longer tracking periods.
- Harder to attribute to specific campaigns.
When to use: Customer success programs, subscription models.
When not to use: Short-term acquisition campaigns.
Cxpify advantage: Recommends predictive retention KPIs, such as propensity to churn or engagement health scores, using AI models that analyze past behavior and cross-channel data.
5. Experience-Driven KPIs
A newer category, measuring how well customers feel understood and valued.
Examples: Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Effort Score (CES), session satisfaction.
Advantages:
- Provides qualitative insight into loyalty and advocacy.
- Helps anticipate future retention and advocacy.
Disadvantages: - Harder to tie directly to revenue.
- Data collection can be intrusive if overused.
Cxpify advantage: AI can recommend which experience KPIs to track per campaign and correlate them with business outcomes, giving a holistic view of ROI beyond conversions.
Part 2: Marketing Attribution Models
Attribution models help you understand which marketing touchpoints contributed to a conversion. Choosing the right model ensures campaigns are optimized for impact.
1. First-Touch Attribution
All credit goes to the first interaction.
Best use: Awareness campaigns.
Avoid when: Multiple touchpoints influence purchase.
2. Last-Touch Attribution
All credit goes to the final interaction.
Best use: Conversion-trigger campaigns.
Avoid when: Long multi-channel customer journeys exist.
3. Linear Attribution
Evenly distributes credit across touchpoints.
Best use: Multi-touch campaigns.
Avoid when: Some touchpoints dominate in influence.
4. Time-Decay Attribution
More credit to interactions closer to conversion.
Best use: Long sales cycles.
Avoid when: Early-stage marketing is critical.
5. Position-Based Attribution
Split credit: first & last touch get more weight, middle interactions get remaining credit.
Best use: Full-funnel campaigns.
Avoid when: Single channel dominates.
6. Data-Driven Attribution
Uses AI/ML to assign credit based on historical data.
Best use: Large-scale multi-channel campaigns.
Avoid when: Data is sparse or tracking is inconsistent.
Cxpify advantage: The platform can recommend the most suitable attribution model per campaign, simulate outcomes across models, and even suggest hybrid models that blend first-touch, last-touch, and AI-driven insights to match your specific business needs.
Conclusion
KPIs tell you what is happening, while attribution models explain why it happened. Platforms like Cxpify make this process smarter by:
- Recommending KPIs that align with campaign goals and customer behavior.
- Suggesting the optimal attribution model based on journey complexity.
- Highlighting new or overlooked metrics, such as micro-conversions or engagement quality scores.
- Providing AI-driven predictions to optimize ROI and future campaigns.
Key takeaway: With intelligent tools, marketers can move beyond guesswork, uncover hidden insights, and make fully informed decisions ultimately driving better outcomes, happier customers, and higher growth.